| [1] 马锡慧,冯凯,石炳毅.人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性及其研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(32):6064-6067.
[2] Zhang YN, Lie PC, Wei X.Differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly into hepatocyte-like cells.Cytotherapy. 2009;11(5):548-558.
[3] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al.Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons.J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.
[4] Paldino E, Cenciarelli C, Giampaolo A,et al.Induction of dopaminergic neurons from human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cell by forskolin.J Cell Physiol. 2014; 229(2):232-244.
[5] Alves da Silva ML, Costa-Pinto AR, Martins A,et al. Conditioned medium as a strategy for human stem cells chondrogenic differentiation.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013 Oct 24. doi: 10.1002/term.1812. [Epub ahead of print].
[6] McElreavey KD, Irvine AI, Ennis KT,et al.Isolation, culture and characterisation of fibroblast-like cells derived from the Wharton's jelly portion of human umbilical cord.Biochem Soc Trans. 1991;19(1):29S.
[7] Mueller SM, Glowacki J.Age-related decline in the osteogenic potential of human bone marrow cells cultured in three- imensional collagen sponges.J Cell Biochem. 2001;82(4): 583-590.
[8] 庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J/CD]/中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2011,1(2):30-33.
[9] 唐欣,王岩,易海波,等.人脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化为心肌细胞的特异性基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(27):4988- 4991.
[10] 王跃春,李业霞,段阿林,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的快速分离、纯化及冻存[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(8):1658-1661.
[11] Shaer A, Azarpira N, Aghdaie MH,et al.Isolation and characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived from Placental Decidua Basalis; Umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly and Amniotic Membrane.Pak J Med Sci. 2014; 30(5):1022-1026.
[12] Tsai PJ, Wang HS, Lin GJ,et al.Undifferentiated Wharton?s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Induces Insulin-Producing Cell Differentiation and Suppression of T Cell-Mediated Autoimmunity in Non-Obese Diabetic Mice.Cell Transplant. 2014 Jul 15. [Epub ahead of print]
[13] Constantinescu A, Andrei E, Iordache F,et al.Recellularization potential assessment of Wharton's Jelly-derived endothelial progenitor cells using a human fetal vascular tissue model.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014 Aug 15. [Epub ahead of print]
[14] Ribeiro J, Pereira T, Amorim I,et al.Cell therapy with human MSCs isolated from the umbilical cord Wharton jelly associated to a PVA membrane in the treatment of chronic skin wounds.Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(10):979-987.
[15] Alunno A, Montanucci P, Bistoni O,et al. In vitro immunomodulatory effects of microencapsulated umbilical cord Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in primary Sjögren's syndrome.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Jul 26. pii: keu292. [Epub ahead of print].
[16] 马海英,李丽,马玲,等.组织块贴壁法提取胎盘、脐带和胎膜间充质干细胞效果观察[J].山东医药,2011,51(15):39-41.
[17] 蒋知新,艾民,张清华,等.体外原代培养脐带基质间充质细胞和人皮肤成纤维细胞[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(19):4193-4194.
[18] 刘玲英,柴家科,段红杰,等.人脐带间充质干细胞不同分离方法的效果比较[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(32):2592-2596.
[19] 侯克东,许文静,张莉,等.人脐带Wharton胶中间充质干细胞向软骨诱导的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(12):930-935.
[20] 郝白露,杨瑞峰,彭祥炽,等.改良的人脐带间充质干细胞培养方法[J].中国计划生育学杂志,2013,21(1):44-49.
[21] 庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2011,1(2):30-33.
[22] 王绮雯,吴启端,陈奕芝.温胰蛋白酶消化法和冷消化法培养乳鼠心肌细胞的比较[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(20):401-403.
[23] 刘巨超,周海洋,孙慧伟,等.工程化肝组织肝表面片状植入新方法[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(5):880-882.
[24] Massood E, Maryam K, Parvin S,et al.Vitrification of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Cryo Letters. 2013;34(5):471-480.
[25] Tantrawatpan C, Manochantr S, Kheolamai P,et al.Pluripotent gene expression in mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and their differentiation potential to neural-like cells.J Med Assoc Thai. 2013;96(9):1208-1217.
[26] Mikaeili Agah E, Parivar K, Nabiuni M,et al.Induction of human umbilical Wharton's jelly-derived stem cells toward oligodendrocyte phenotype.J Mol Neurosci. 2013;51(2): 328-336.
[27] Messerli M, Wagner A, Sager R,et al.Stem cells from umbilical cord Wharton's jelly from preterm birth have neuroglial differentiation potential.Reprod Sci. 2013;20(12):1455-1464.
[28] Kim MJ, Shin KS, Jeon JH,et al.Human chorionic-plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells and Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a comparative analysis of their potential as placenta-derived stem cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2011;346(1):53-64.
[29] Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS.Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow.Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392.
[30] De Bruyn C, Najar M, Raicevic G,et al.A rapid, simple, and reproducible method for the isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells from Wharton's jelly without enzymatic treatment.Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(3):547-557.
[31] Weiss ML, Anderson C, Medicetty S, et al.Immune properties of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived cells.Stem Cells. 2008;26(11):2865-2874.
[32] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E,et al.Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):319-331.
[33] Hu Y, Liang J, Cui H,et al.Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into retinal progenitor cells.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(19):1783-1792.
[34] Joerger-Messerli M, Brühlmann E, Bessire A,et al. Preeclampsia enhances neuroglial marker expression in umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014:1-6.
[35] Yan M, Sun M, Zhou Y,et al.Conversion of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton's jelly to dopamine neurons mediated by the Lmx1a and neurturin in vitro: potential therapeutic application for Parkinson's disease in a rhesus monkey model.PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64000.
[36] Balasubramanian S, Thej C, Venugopal P,et al.Higher propensity of Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stromal cells towards neuronal lineage in comparison to those derived from adipose and bone marrow.Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(5): 507-515.
[37] 周剑云,孙炜,张新,等.人脐带源神经干细胞的培养和分化[J].中国康复理论与实践,2012, 18(7): 615-618.
[38] 李伟伟,姚星宇,杨丽敏,等.体外诱导人脐带间充质干细胞向神经干细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(1):75-80. |
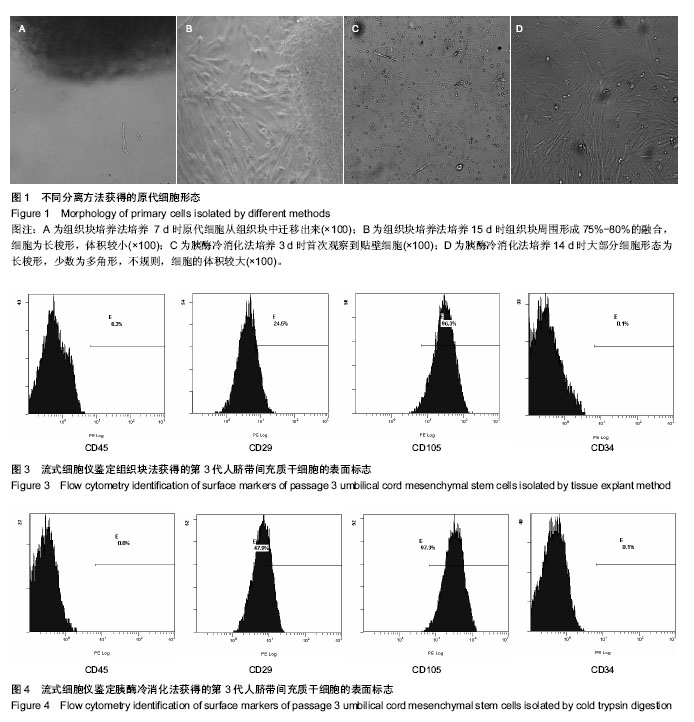
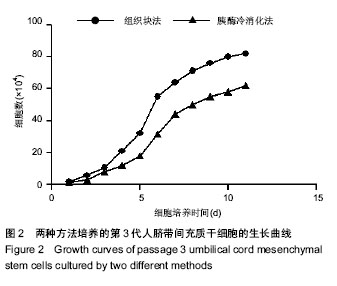
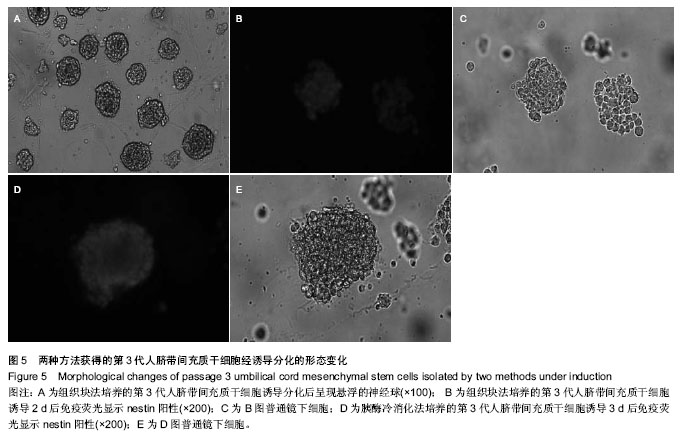
.jpg)